This tutorial is shared to learn SQL HAVING statement with definition, query, syntax & example. Even You will learn to use it with aggregate functions like COUNT(), SUM(), MAX, MIN() & AVG().
The HAVING clause always executes in the SELECT statement with the GROUP BY clause and returns the result of grouped values based on conditions. So, Before learning it, you must have a basic knowledge of the GROUP BY clause.
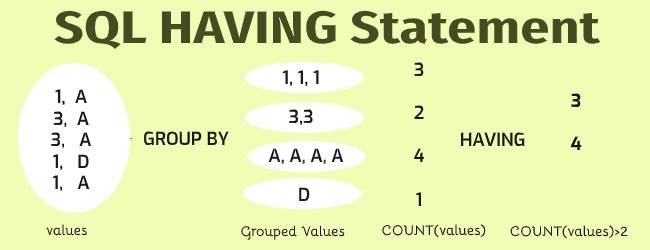
What is SQL HAVING Clause
Definition – The SQL Having clause returns by grouping values based on specified conditions using aggregate functions
Learn also –
SQL Interview Questions and Answers
You must memorize the following points –
- GROUP BY clause is required to execute the HAVING statement.
- The HAVING always comes with aggregate functions like COUNT(), SUM(), MIN(), MAX() & AVG()
- HAVING Clause is always used with a SELECT Statement.
- You should use HAVING after WHERE GROUP BY clause if you need to use it.
- You should also use HAVING before the ORDER BY clause if you need to use it.
SQL HAVING Syntax
This SQL HAVING syntax is created with two columns of a table. once, you learn, You definitely create for more columns.
SELECT column_name1, column_name2,... FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column_name1, column_name2... HAVING condition ORDER BY column_name1, column_name2...;
SQL HAVING Example
I have created a table employees with duplicate values for a SQL HAVING example. This table has five columns like empolyee_id, full_name, gender, city & salary.
You can create a table using the following query.
CREATE TABLE employees
(
employee_id int(10) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
full_name varchar(50),
gender varchar(20),
city varchar(100),
salary int(10)
);
You can also insert some values in employees table using the following query
INSERT INTO employees( full_name, gender, city, salary) VALUES
( 'Noor Khan', 'Male', 'Patna', 30000),
('Sunil Kumar', 'Male', 'New Delhi', 45000),
( 'Monika Singh', 'Female', 'Chennai', 30000),
('Aaliya Khan', 'Female', 'Chennai', 40000),
( 'Sunil Kumar', 'Male', 'Patna', 25000),
('Monika Singh', 'Female', 'New Delhi', 60000),
('Rapson Jani', 'Male', 'Patna', 70000),
('Rapson Jani', 'Male', 'New Delhi', 25000),
('Sunil Kumar', 'Male', 'Patna', 65000),
('Monika Singh', 'Female', 'Patna', 32000);
Table Structure –
This is the table structure with some data of employees
Table Name – employees
| employee_id | full_name | gender | city | salary |
| 201 | Noor Khan | Patna | 30,000 | |
| 202 | Sunil Kumar | New Delhi | 45,000 | |
| 203 | Monika Singh | Chennai | 30,000 | |
| 204 | Aaliya Khan | Chennai | 40,000 | |
| 205 | Sunil Kumar | Patna | 25,000 | |
| 206 | Monika Singh | New Delhi | 60,000 | |
| 207 | Rapson Jani | Patna | 70,000 | |
| 208 | Rapson Jani | New Delhi | 25,000 | |
| 209 | Sunil Kumar | Patna | 65,000 | |
| 210 | Monika Singh | Patna | 32,000 |
Query –
If you need to know the names of the city in which more than 2 employees live, use the following query
SELECT city, COUNT(full_name) FROM employees GROUP BY city HAVING COUNT(full_name)>2;
Output –
| city | COUNT(full_name) |
| New Delhi | 3 |
| Patna | 5 |
SQL HAVING Aggregate Functions
You have already learned in the previous step that the HAVING clause needs aggregate functions to returns the result of grouped values. Now, You will see it with an example
GROUP BY COUNT()
If you need to know the total number of records of any specified column based on the HAVING clause, use the COUNT() function.
Example –
We have to display only full names of more than two employees who have the same name.
Query –
SELECT full_name, COUNT(full_name) FROM employees GROUP BY full_name HAVING COUNT(full_name)>2;
Output –
| full_name | COUNT(full_name) |
| Sunil Kumar | 3 |
| Monika Singh | 3 |
HAVING SUM()
If you need to know the total sum values of any specified column based on the HAVING clause, use the SUM() function.
Example – 1
We have to add total salary employees who have the same name and total salary must be greater than 40,000
Query –
SELECT full_name, SUM(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY full_name HAVING SUM(salary)>40000
Output –
| full_name | SUM(salary) |
| Monika Singh | 122000 |
| Rapson Jani | 35000 |
| Sunil Kumar | 135000 |
HAVING MIN()
If you need to know the lowest value of any specified column based on the HAVING clause, use MIN() function.
Example –
We have to display maximum salary employees who have the same name and Maximum salary must be greater than 40,000
Query –
SELECT full_name, MAX(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY full_name HAVING MAX(salary)>40000
Output –
| full_name | MAX(salary) |
| Monika Singh | 60000 |
| Rapson Jani | 70000 |
| Sunil Kumar | 65000 |
HAVING MAX()
If you need to know the largest value of any specified column based on the HAVING clause, use the MAX() function.
Example –
We have to display minimum salary employees who have the same name and Minimum salary must be less than 30,000
Query –
SELECT full_name, MIN(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY full_name HAVING MIN(salary)<30000
Output –
+----------------+---------------- -----+ | full_name | MIN(salary) | +----------------+----------------------+ | Rapson Jani | 25000 | | Sunil Kumar | 25000 | +----------------+----------------------+
HAVING AVG()
If you need to know the average value of any specified column based on the HAVING clause, use the AVG() function.
Example –
We have to display average salary employees who have the same name and Average salary must be greater than 40,000
Query –
SELECT full_name, AVG(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY full_name HAVING AVG(salary)>40000
Output –
| full_name | AVG(salary) |
| Monika Singh | 40666.66 |
| Rapson Jani | 47500 |
| Sunil Kumar | 45000 |
SQL HAVING with different clauses
In some cases, You may need to use SQL HAVING statement with WHERE & ORDER BY clause. So, you should know about it with an example
HAVING with WHERE Clause
You may use the HAVING clause with the WHERE clause. Let’s understand it through the following Syntax & example
Syntax –
SELECT column_name1, column_name2.. FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column_name1, column_name2.. HAVING condition;
Example –
We have to display only full names of more than two employees who have the same name and those employees must be Male.
Query –
SELECT full_name, COUNT(full_name) FROM employees WHERE gender='Male' GROUP BY full_name HAVING COUNT(full_name)>2;
Output –
| full_name | COUNT(full_name) |
| Monika Singh | 3 |
HAVING with ORDER BY Clause
You may also use the HAVING clause with the ORDER BY clause. Let’s understand it through the following syntax & example.
Syntax –
SELECT column_name1, column_name2.. FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name1, column_name2.. HAVING condition; ORDER BY column_name1, column_name2..
Example –
We have to display maximum salary employees who have the same name. A maximum salary must be in descending order and greater than 40,000.
Query –
SELECT full_name, MAX(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY full_name HAVING MAX(salary)>40000 ORDER BY salary DESC;
Output –
| full_name | MAX(salary) |
| Rapson Jani | 70,000 |
| Sunil Kumar | 65,000 |
| Monika Singh | 60,000 |
HAVING with WHERE and ORDER BY clause
You may also use the HAVING clause with both WHERE & ORDER BY clause. Let’s understand it through the following syntax & example.
Syntax –
SELECT column_name1, column_name2.. FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column_name1, column_name2.. HAVING condition; ORDER BY column_name1, column_name2..
Example –
We have to display maximum salary employees who have the same name. Those employees must be Male and A maximum salary must be in descending order & greater than 40,000.
Query –
SELECT full_name, MAX(salary) FROM employees WHERE gender='Male' GROUP BY full_name HAVING MAX(salary)>40000 ORDER BY salary DESC;
Output –
| full_name | MAX(salary) |
| Rapson Jani | 70,000 |
| Sunil Kumar | 65,000 |
How to Execute SQL HAVING clause
To execute SQL HAVING, you have to configure the following points –
- First of all, install SQL server package in your computer
- Create a MySQL Database like
my_db - Create a table like
employeesin MySQL database - Insert some records in the created table
- Write a SELECT query command with HAVING, WHERE, GROUP BY, & ORDER BY clause
mysql>CREATE DATABASE my_db;
mysql>USE my_db;
mysql>CREATE TABLE employees
(
full_name varchar(50),
gender varchar(20),
city varchar(100),
salary int(10)
);
mysql>INSERT INTO employees( full_name, gender, city, salary) VALUES
( 'Noor Khan', 'Male', 'Patna', 30000),
('Sunil Kumar', 'Male', 'New Delhi', 45000),
( 'Monika Singh', 'Female', 'Chennai', 30000),
('Aaliya Khan', 'Female', 'Chennai', 40000),
( 'Sunil Kumar', 'Male', 'Patna', 25000),
('Monika Singh', 'Female', 'New Delhi', 60000),
('Rapson Jani', 'Male', 'Patna', 70000),
('Rapson Jani', 'Male', 'New Delhi', 25000),
('Sunil Kumar', 'Male', 'Patna', 65000),
('Monika Singh', 'Female', 'Patna', 32000);
mysql>SELECT full_name, MAX(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE gender='Male'
GROUP BY full_name
HAVING MAX(salary)>40000
ORDER BY salary DESC;
Tutorial Summary
Dear Developer, I have this tutorial according to my working experience. I hope that You have learned how to use SQL HAVING clause with SELECT statement.
If you have any questions related to SQL, Kindly ask me through the comment box. Even you can suggest sharing another web development tutorial.
