SQL INNER JOIN is frequently used to join two or more tables. It is mainly used with the SELECT statement to select data from multiple tables. So, you should have knowledge of the SELECT statement. if you don’t have then you will not worry about it. Here I will give you basic information about it so that you can easily use it to select data by joining multiple tables.
In this tutorial, you will learn everything like inner joins multiple tables with a definition, example, query & execution using the command line. I have explained all the related information in detail that will be easy to understand and you will become an expert on this topic.
Read Also –
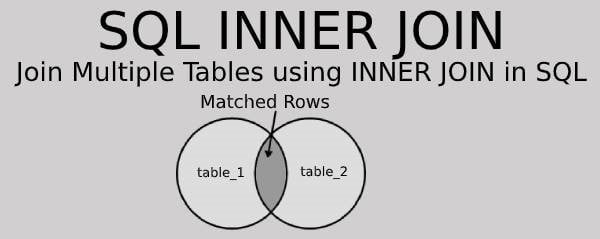
Definition of SQL INNER JOIN
SQL INNER JOIN selects all the records of two or more tables if matching values remain in each common column of all the tables.
The INNER JOIN creates a new table by combining selected columns of multiple tables. But each row value of one table must be matched with the corresponding row value of another table.
INNER JOIN jus a keyword that helps to join more than one table. It is mainly used with the SELECT statement.
If you want to select data from multiple tables then you will have to write multiple SELECT queries. But you can select data by writing a single select statement when you use INNER join with it.
Let’s understand it with a basic example.
Suppose that we have three tables like table_1, table_2 & table_3. A common column id1 belongs to each table.
- The first table
table_1has three columns likeid1,column_1,column_2. - The second
table_2has five values likeid2,id1,column_1,column_2,column_3. - The third table
table_3has six columns likeid3,id1,column_1,column_2,column_3,column_4
SELECT statement without INNER JOIN
If we select data from those three tables without INNER JOIN then we will have to write the following three select query –
// The first query SELECT id1, column_1, column_2 FROM table_1; // The second query SELECT id2, id1, column_1, column_2, column_3 FROM table_2; // The third query SELECT id3, id1, column_1, column_2, column_3, column_4 FROM table_3;
SELECT statement with INNER JOIN
If we select data from those three tables with INNER JOIN then we can write the following a single SELECT query –
SELECT table_1.id1, table_1.column_1, table_1.column_2,
table_2.id2, table_2.column_1, table_2.column_2, table_2.column_3,
table_3.id3, table_3.column_1, table_3.column_2, table_3.column_3, table_3.column_4
FROM table_1
INNER JOIN table_2 ON table_1.id1 = table_2.id1
INNER JOIN table_3 ON table_1.id1 = table_3.id1;
Syntax –
You can use one of the following syntaxes
Syntax – 1
If you use this syntax then it will match each row value of the first_table with corresponding row value of second_table. So, first_table will be left table and second_table will be the right table.
SELECT * FROM first_table INNER JOIN second_table ON first_table.column_name=second_table.column_name;
Syntax – 2
If you use this syntax then it will match each row value of the second_table with corresponding row value of first_table. So, first_table will be left table and second_table will be the right table.
SELECT * FROM second_table INNER JOIN first_table ON second_table.column_name = first_table.column_name;
Important Points –
- All the tables should be in a relationship with a foreign key.
- One column of each table must contain the matching values.
- Datatypes of the corresponding column in each table may be the same or different.
- The number of columns in each table may be the same or different.
- Corresponding column names of each table may be the same or different.
- The number of records in each table may be the same or different.
- Each table may have distinct values, duplicate values, or a combination of both values.
Query
To write the SQL INNER JOIN query, we have to take an example to make it easy for creating a query.
Suppose that we have to join n number of tables like table_1, table_2, table_3, table_4……, table_n. All the tables have n number of column-like column_1, column_2, column_3, column_4…..column_n.
Query to join Two Tables
Query – 1
You should use this query if you have to select rows values of all the columns from two tables.
SELECT * FROM table_1 INNER JOIN table_2 ON table_1.matching_column = table_2.matching_column;
Query -2
You should use this query if you have to select rows values of a specified column from two tables.
SELECT table_1.column_1, table_1.column_2, table_1.column_3, ...table1.column_n
table_2.column_1, table_2.column_2, table_2.column_3, ...table2.column_n
FROM table_1
INNER JOIN table_2
ON table_1.matching_column = table_2.matching_column;
Query to join Three Tables
Query – 1
You should use this query if you have to select rows values of all the columns from three tables.
SELECT * FROM table_1 INNER JOIN table_2 ON table_1.matching_column = table_2.matching_column INNER JOIN table_3 ON table_1.matching_column = table_3.matching_column;
Query – 2
You should use this query if you have to select rows values of a specified column from two tables.
SELECT table_1.column_1, table_1.column_2, table_1.column_3, ...table1.column_n
table_2.column_1, table_2.column_2, table_2.column_3, ...table2.column_n
table_3.column_1, table_3.column_2, table_3.column_3, ...table3.column_n
FROM table_1
INNER JOIN table_2
ON table_1.matching_column = table_2.matching_column
INNER JOIN table_3
ON table_3.matching_column = table_3.matching_column;
Query For multiple Tables
Query – 1
You should use this query if you have to select rows values of all the columns from n tables.
SELECT * FROM table_1 INNER JOIN table_2 ON table_1.matching_column = table_2.matching_column INNER JOIN table_3 ON table_1.matching_column = table_3.matching_column ..... ..... ..... INNER JOIN table_n ON table_1.matching_column = table_n.matching_column;
Query – 2
You should use this query if you have to select rows values of the specified column from n tables.
SELECT table_1.column_1, table_1.column_2, table_1.column_3, ...table1.column_n
table_2.column_1, table_2.column_2, table_2.column_3, ...table2.column_n
table_3.column_1, table_3.column_2, table_3.column_3, ...table3.column_n
.........
table_n.column_1, table_n.column_2, table_n.column_3, ...tablen.column_n
FROM table_1
INNER JOIN table_2
ON table_1.matching_column = table_2.matching_column;
INNER JOIN table_3
ON table_1.matching_column = table_3.matching_column;
......
......
INNER JOIN table_n
ON table_1.matching_column = table_n.matching_column;
Types of INNER JOIN?
INNER Join is divided into two main parts –
EQUI JOIN
In the case of Equi Join, INNER JOIN will select those rows that have matching data in a common column of both tables
Syntax –
SELECT first_table.column_1, first_table.column_2, ...., first_table.column_n
second_table.column_2, second_table.column_2, ...., second_table.columnn
FROM first_table
INNER JOIN
second_table
ON first_table.column_name = second_table.column_name;
NON-EQUI JOIN
In the case of Equi Join, INNER JOIN will select those rows that don’t have matching data in a common column of both tables
Syntax –
SELECT first_table.column_1, first_table.column_2, ...., first_table.column_n
second_table.column_2, second_table.column_2, ...., second_table.columnn
FROM first_table
INNER JOIN
second_table
ON first_table.column_name <> second_table.column_name;
SQL INNER JOIN Example
Here is the best SQL INNER JOIN example for your better understanding. With this example, you will definitely become export in INNER JOIN tops. So, you must implement it on your computer.
Now, Let’s start with the following example –
Suppose that we have two tables like employees and departments. Both tables store some values in the following table structure.
Table Name – employees
| employee_id | employee_name | gender | city |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sumit Mishra | Male | Noida |
| 2 | Monika Singh | Female | Delhi |
| 3 | Ayush Aryan | Male | Chennai |
| 4 | Rapson Jani | Male | Patna |
| 5 | Sonali Mishra | Female | Patna |
Table Name – departments
| department_id | department_name | employee_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Technology | 4 |
| 2 | HR | 2 |
| 3 | Admin | 1 |
| 4 | Marketing | 3 |
| 5 | Engineering | 5 |
Equi Join Example –
In this example, we will join both tables using Equi join syntax.
SELECT employees.employee_name, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.employee_id = departments.department_name;
Output –
| employee_name | department_name |
|---|---|
| Rapson Jani | Technology |
| Monika Singh | HR |
| Sumit Mishra | Admin |
| Ayush Aryan | Marketing |
| Sonali Mishra | Engineering |
Non-Equi Join Example –
In this example, we will join both tables using Non-Equi Join syntax.
SELECT employees.employee_name, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.employee_id <> departments.department_name;
Output –
| employee_name | department_name |
|---|---|
| Sumit Mishra | Technology |
| Sumit Mishra | HR |
| Sumit Mishra | Marketing |
| Sumit Mishra | Engineering |
| Monika Singh | Technology |
| Monika Singh | Admin |
| Monika Singh | Marketing |
| Monika Singh | Engineering |
| Ayush Aryan | Technology |
| Ayush Aryan | HR |
| Ayush Aryan | Admin |
| Ayush Aryan | Engineering |
| Rapson Jani | HR |
| Rapson Jani | Admin |
| Rapson Jani | Marketing |
| Rapson Jani | Engineering |
| Sonali Mishra | Technology |
| Sonali Mishra | HR |
| Sonali Mishra | Admin |
| Sonali Mishra | Marketing |
INNER JOIN with Different Clauses
We can also use INNER JOIN with the different clauses. We will join both tables employees & departments that are created in the previous example.
INNER JOIN with WHERE
You can also use an INNER JOIN with where clause. Using the following query, You will get a new result table where the column gender has values male.
SELECT employees.employee_name, employees.gender, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.employee_id = departments.department_name WHERE employees.gender = 'male';
INNER JOIN with ORDER BY
You can also use an INNER JOIN with the ORDER BY clause. Using the following query, You will get a new result table with the alphabetical order of employee_name.
SELECT employees.employee_name, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.employee_id = departments.department_name ORDER BY employees.employee_name;
INNER JOIN with GROUP BY
You can also use an INNER JOIN with the GROUP BY clause. Using the following query, You will get a new result table group by gender.
SELECT count(employees.employee_id), employees.gender FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.employee_id = departments.department_name GROUP BY employees.gender;
INNER JOIN with LIMIT
You can also use an INNER JOIN with the LIMIT clause. Using the following query, You will get a new result table with 3 records
SELECT employees.employee_name, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.employee_id = departments.department_name LIMIT 3;
INNER JOIN with Alias
As you know that Alias is a temporary name of a table, column. It makes long table name & column name more readable. So, you should use INNER JOIN with Alias.
Query – 1
SELECT emp.employee_name, dept.department_name FROM employees AS emp INNER JOIN departments AS dept ON emp.employee_id = dept.department_name;
Query – 2
SELECT emp.employee_name AS employeeName, dept.department_name AS departmentName FROM employees AS emp INNER JOIN departments AS dept ON emp.employee_id = dept.department_name;
SQL INNER JOIN Multiple Tables
You can join multiple tables using an INNER JOIN. To understand it, we have to see an example. Here I will learn you how to join 2 & 3 tables. once you learn it you will quickly join more tables.
Example –
There are three tables like courses, subjects, & chapters. Each table is related to each other with matching values. Join all these tables using INNER JOIN.
See the following table structure of each table.
Table Name – courses
This table is created with two columns like course_id, course_name.
| course_id | course_name |
| 1 | Web Designing |
| 2 | Web Development |
| 3 | Database |
| 4 | Programming |
Table Name – subjects
This table is created with three columns like subject_id, course_id, subject_name.
| subject_id | course_id | subject_name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | HTML |
| 2 | 1 | CSS |
| 3 | 1 | JavaScript |
| 4 | 1 | jQuery |
| 5 | 2 | PHP |
| 6 | 2 | Node.js |
| 7 | 3 | MySQL |
| 8 | 3 | MongoDB |
| 9 | 4 | C++ |
| 10 | 4 | Python |
| 11 | 4 | Java |
Table Name – chapters
This table is created with four columns like subject_id, course_id, subject_name.
| chapter_id | course_id | subject_id | subject_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | HTML Intro |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | HTML tag |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | HTML Paragraph |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | HTML table |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | CSS Intro |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | CSS Selectors |
| 7 | 1 | 2 | CSS Background |
| 8 | 1 | 2 | CSS Color |
| 9 | 1 | 2 | CSS Padding |
| 10 | 1 | 2 | CSS Margin |
| 11 | 1 | 3 | JavaScript Intro |
| 12 | 1 | 3 | JavaScript Variables |
| 13 | 1 | 3 | JavaScript Operators |
| 14 | 1 | 3 | JavaScript Datatype |
| 15 | 1 | 4 | jQuery Intro |
| 16 | 1 | 4 | jQuery Selectors |
| 17 | 1 | 4 | jQuery Events |
| 18 | 2 | 5 | PHP Intro |
| 19 | 2 | 5 | PHP Variables |
| 20 | 2 | 5 | PHP String |
| 21 | 2 | 5 | PHP Functions |
| 22 | 2 | 6 | Node.js Intro |
| 23 | 2 | 6 | Node.js Modules |
| 24 | 2 | 6 | Node.js File System |
| 25 | 3 | 7 | MySQL Intro |
| 26 | 3 | 7 | MySQL Syntax |
| 27 | 3 | 8 | MongoDB Intro |
| 28 | 3 | 8 | MongoDB Syntax |
| 29 | 4 | 9 | C++ Intro |
| 30 | 4 | 9 | C++ Variables |
| 31 | 4 | 9 | C++ Datatype |
| 32 | 4 | 10 | Python Intro |
| 33 | 4 | 10 | Python Variables |
| 34 | 4 | 10 | Python Datatypes |
| 35 | 4 | 11 | Java Intro |
| 36 | 4 | 11 | Java variables |
| 37 | 4 | 11 | Java Datatypes |
JOIN 2 Tables
SQL INNER JOIN 2 Tables – If you want to use INNER JOIN on 2 tables in SQL then you can use the following query. This query will join two tables courses & subjects.
SELECT courses.course_name, subjects.subject_name FROM subjects INNER JOIN courses ON subjects.course_id = subjects.course_id;
JOIN 3 Tables
SQL INNER JOIN 3 Tables – If you want to use INNER JOIN on 3 tables in SQL then you can use the following query. This query will join two tables courses , subjects and chapters.
SELECT courses.course_name, subjects.subject_name, chapters.chapter_name FROM chapters INNER JOIN courses ON chapters.course_id = courses.course_id INNER JOIN subjects ON chapters.subject_id = subjects.subject_id;
How to Execute an INNER JOIN?
You will have to configure the following steps if you want to execute INNER JOIN –
- First of all, Make sure that SQL Server is installed on your computer.
- Create a Database my_db
- Create two tables for employees & departments
- Insert the required values in both tables
- Write SELECT statements with INNER JOIN
Execution INNER JOIN using Equi Join –
mysql>CREATE DATABASE my_db;
mysql>USE my_db;
mysql>CREATE TABLE employees
->(
->employee_id int(10) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
->employee_name varchar(50),
->gender varchar(10),
->city varchar(100)
->);
mysql>INSERT INTO employees(employee_name, gender, city)
->VALUES('Sumit Mishra', 'Male', 'Noida'),
->('Monika Singh', 'Female', 'Delhi'),
->('Ayush Aryan', 'Male', 'Chennai'),
->('Rapson Jani', 'Male', 'Patna'),
->('Sonali Mishra', 'Female', 'Patna');
mysql>CREATE TABLE departments
->(
->department_id int(10) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
->department_name varchar(50),
->employee_id int,
->CONSTRAINT employee_id_fk
->FOREIGN KEY(employee_id) REFFERENCES employees(employee_id)
->);
mysql>INSERT INTO departments(department_name, employee_id)
->VALUES('Technology', 4 ),
->('HR', 2),
->('Admin', 1),
->('Marketing', 3),
->('engineering', 5);
mysql>SELECT * FROM employees;
mysql>SELECT * FROM departments
mysql>SELECT employees.employee_name, departments.department_name
->FROM employees
->INNER JOIN
->departments ON employees.employee_id = departments.department_name;
Execution INNER JOIN using Non-Equi Join –
mysql>use my_db;
mysql>SELECT employees.employee_name, departments.department_name
->FROM employees
->INNER JOIN
->departments ON employees.employee_id <> departments.department_name;
Tutorial Summary
Dear Developer, I have this tutorial according to my working experience. I hope that It will be useful to implement INNER JOIN in SQL. Even this tutorial will be more helpful for the Interview.
If you have any questions related to SQL, Kindly ask me through the comment box. Even you can suggest sharing another web development tutorial.
